AWS ECS/Fargate
This workflow is currently in preview status. Please provide feedback in our slack community.
Prerequisites
Working with ECS
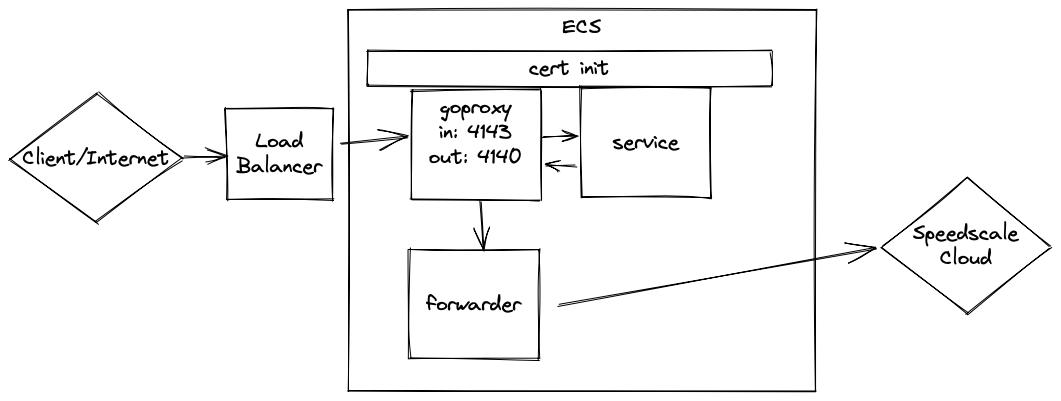
To capture traffic for a service running in ECS, we need to setup some components shown above. The examples snippets in this guide will be in the form of Terraform but all the parameters used have equivalents in CloudFormation, the AWS CLI, the AWS console, etc.
Setup the forwarder
The forwarder handles sending captured traffic up to Speedscale cloud and only a single forwarder is needed regardless of the number of services being captured. The Terraform below creates an ECS task definition, an ECS service and adds it to a private hosted zone for service discovery. Make sure to replace SPEEDSCALE_API_KEY, TENANT_BUCKET, TENANT_NAME, etc. with values from ~/.speedctl/config which should have been populated during speedctl setup.
The service discovery hosted zone used for our example is ecs.local and our ECS service discovery block will setup forwarder.ecs.local which will be used in the next step.
resource "aws_ecs_task_definition" "forwarder" {
family = "forwarder"
execution_role_arn = aws_iam_role.exec.arn
requires_compatibilities = ["FARGATE"]
network_mode = "awsvpc"
cpu = 256
memory = 512
container_definitions = jsonencode([
{
name = "forwarder"
image = "gcr.io/speedscale/forwarder:v2.3.586"
essential = true
healthCheck = {
command = [
"CMD-SHELL",
"curl -v localhost:8888 2>&1 | grep Connected"
]
}
portMappings = [
{
containerPort = 8888
}
],
environment = [
{
name = "CLUSTER_NAME"
value = "ecs"
},
{
name = "SPEEDSCALE_API_KEY"
value = "yourkey"
},
{
name = "SPEEDSCALE_APP_URL"
value = "app.speedscale.com"
},
{
name = "SUB_TENANT_NAME"
value = "default"
},
{
name = "SUB_TENANT_STREAM"
value = "sstenant-tenant"
},
{
name = "TENANT_BUCKET"
value = "sstenant-tenant"
},
{
name = "TENANT_NAME"
value = "sstenant-tenant"
},
{
name = "TENANT_ID"
value = "uuid"
},
{
name = "TENANT_REGION"
value = "us-east-1"
},
],
},
])
}
resource "aws_service_discovery_service" "forwarder" {
name = "forwarder"
namespace_id = aws_service_discovery_private_dns_namespace.cluster.id
dns_config {
namespace_id = aws_service_discovery_private_dns_namespace.cluster.id
dns_records {
ttl = 10
type = "A"
}
}
}
resource "aws_ecs_service" "forwarder" {
name = "forwarder"
cluster = aws_ecs_cluster.cluster.id
task_definition = aws_ecs_task_definition.forwarder.arn
force_new_deployment = true
desired_count = 1
launch_type = "FARGATE"
service_registries {
registry_arn = aws_service_discovery_service.forwarder.arn
container_name = "forwarder"
}
network_configuration {
subnets = data.aws_subnet_ids.private.ids
security_groups = [var.sg_id]
}
}
Create TLS secrets
To capture outbound TLS calls, we need to setup TLS certs to be used by the services. These certs will be placed in AWS Secrets Manager and then used by the ECS tasks. We will get the TLS certs generated from an existing deployment of the Speedscale Operator in a Kubernetes cluster. If you have not installed the Operator anywhere, you can generate these certs with openssl.
You can also use S3 instead of Secrets Manager here
openssl genrsa -out tls.key 4096
openssl req -new -key tls.key -x509 -days 365 -out tls.crt -subj "/C=US/ST=Georgia/L=Atlanta/O=Speedscale/CN=speedscale.com"
OR
kubectl -n speedscale get secret speedscale-certs -o json | jq -r '.data["tls.crt"]' | base64 -D >> tls.crt
kubectl -n speedscale get secret speedscale-certs -o json | jq -r '.data["tls.key"]' | base64 -D >> tls.key
THEN
aws secretsmanager create-secret --name tls.crt --secret-string file://tls.crt
aws secretsmanager create-secret --name tls.key --secret-string file://tls.key
Create new Task Definition
In the example below, the service we want to capture is called notifications and it serves on port 8080. Here are the pieces added to the task:
- An init container that populates the task volume with the TLS certs we created in Secrets Manager in the previous step.
- TLS configuration for the
notificationsservice with the environment variables forSSL_CERT_FILE,HTTP_PROXYandHTTPS_PROXY. These variables depend on the language of your app so refer to proxy server configuration and trusting TLS certificates. - A
goproxysidecar that will capture inbound and outbound traffic. The environment variables for this container need to be edited per environment.APP_LABEL,APP_POD_NAMEandAPP_POD_NAMESPACEcan be set to whatever values you want to differentiate different captured traffic by.REVERSE_PROXY_PORTmust be the port on which the app being captured serves.FORWARDER_ADDRneeds to be whatever the service discovery name for the forwarder we setup previously is, in this caseforwarder.ecs.local:8888.
The role used by your task needs to have secretsmanager:GetSecretValue and kms:Decrypt permissions in order to access the TLS secrets.
resource "aws_ecs_task_definition" "with-speedscale" {
family = "notifications-capture"
execution_role_arn = aws_iam_role.exec.arn
task_role_arn = aws_iam_role.exec.arn
network_mode = "awsvpc"
requires_compatibilities = ["FARGATE"]
cpu = 256
memory = 512
container_definitions = jsonencode([
{
entrypoint = ["bash"]
command = ["-c", "aws secretsmanager get-secret-value --secret-id tls.crt --query SecretString --output text >> /etc/ssl/speedscale/tls.crt && aws secretsmanager get-secret-value --secret-id tls.key --query SecretString --output text >> /etc/ssl/speedscale/tls.key"],
mountPoints = [
{
containerPath = "/etc/ssl/speedscale",
sourceVolume = "speedscale"
}
],
image = "amazon/aws-cli:2.8.4",
essential = false,
name = "init"
},
{
name = "notifications"
image = "gcr.io/speedscale-demos/notifications"
essential = true
environment = [
{
name = "SSL_CERT_FILE"
value = "/etc/ssl/speedscale/tls.crt"
},
{
name = "HTTP_PROXY"
value = "http://localhost:4140"
},
{
name = "HTTPS_PROXY"
value = "http://localhost:4140"
},
],
dependsOn = [
{
containerName = "init",
condition = "SUCCESS"
},
{
containerName = "goproxy",
condition = "START"
},
]
portMappings = [
{
containerPort = 8080
}
]
mountPoints = [
{
containerPath = "/etc/ssl/speedscale",
sourceVolume = "speedscale"
}
],
},
{
name = "goproxy"
image = "gcr.io/speedscale/goproxy:v2.3.586"
essential = true
logConfiguration = {
logDriver = "awslogs",
options = {
awslogs-create-group = "true",
awslogs-group = "ecs/goproxy"
awslogs-region = "us-east-1",
awslogs-stream-prefix = "ecs"
},
},
dependsOn = [
{
containerName = "init",
condition = "SUCCESS"
}
]
mountPoints = [
{
containerPath = "/etc/ssl/speedscale",
sourceVolume = "speedscale"
}
],
portMappings = [
{
containerPort = 4143
},
{
containerPort = 4140
}
]
environment = [
{
name = "LOG_LEVEL"
value = "info"
},
{
name = "APP_LABEL"
value = "notifications"
},
{
name = "APP_POD_NAME"
value = "notifications"
},
{
name = "APP_POD_NAMESPACE"
value = "ecs"
},
{
name = "CAPTURE_MODE"
value = "proxy"
},
{
name = "PROXY_TYPE"
value = "dual"
},
{
name = "PROXY_PROTOCOL"
value = "tcp:http"
},
{
name = "TLS_OUT_UNWRAP"
value = "true"
},
{
name = "REVERSE_PROXY_PORT"
value = "8080"
},
{
name = "FORWARDER_ADDR"
value = "forwarder.ecs.local:8888"
},
]
},
],
)
volume {
name = "speedscale"
}
}
Modify the ECS service
Now the ECS service needs to be modified to use the new task definition and the load balancer configuration needs to point to goproxy:4143 instead of what was in our case notifications:8080.
resource "aws_ecs_service" "notifications" {
name = "notifications"
cluster = aws_ecs_cluster.cluster.id
task_definition = aws_ecs_task_definition.with-speedscale.arn
force_new_deployment = true
desired_count = 1
launch_type = "FARGATE"
load_balancer {
target_group_arn = aws_lb_target_group.default.arn
container_name = "goproxy"
container_port = 4143
}
network_configuration {
subnets = data.aws_subnet_ids.private.ids
security_groups = [var.sg_id]
}
}
Verification
Now if you send requests to your app as you did previously through the load balancer, they will be captured and sent to Speedscale.
Running a test
After capturing traffic and creating a snapshot, we can run a test against our service. We'll do the following:
- Create a task definition for a
generatorwhich is the Speedscale component that will generate load against the service. - Run this as a one off task.
This task will have a set of environment variables to be filled from your ~/.speedctl/config just like we did when setting up the forwarder as well as three additional ones: SNAPSHOT_ID which comes from the snapshot created with traffic, a TEST_CONFIG_ID which specifies the behavior of your test and CUSTOM_URL which will is the URL of the service to be tested. In this case it's http://notifications.ecs.local because we've setup ECS service discovery for our notifications service.
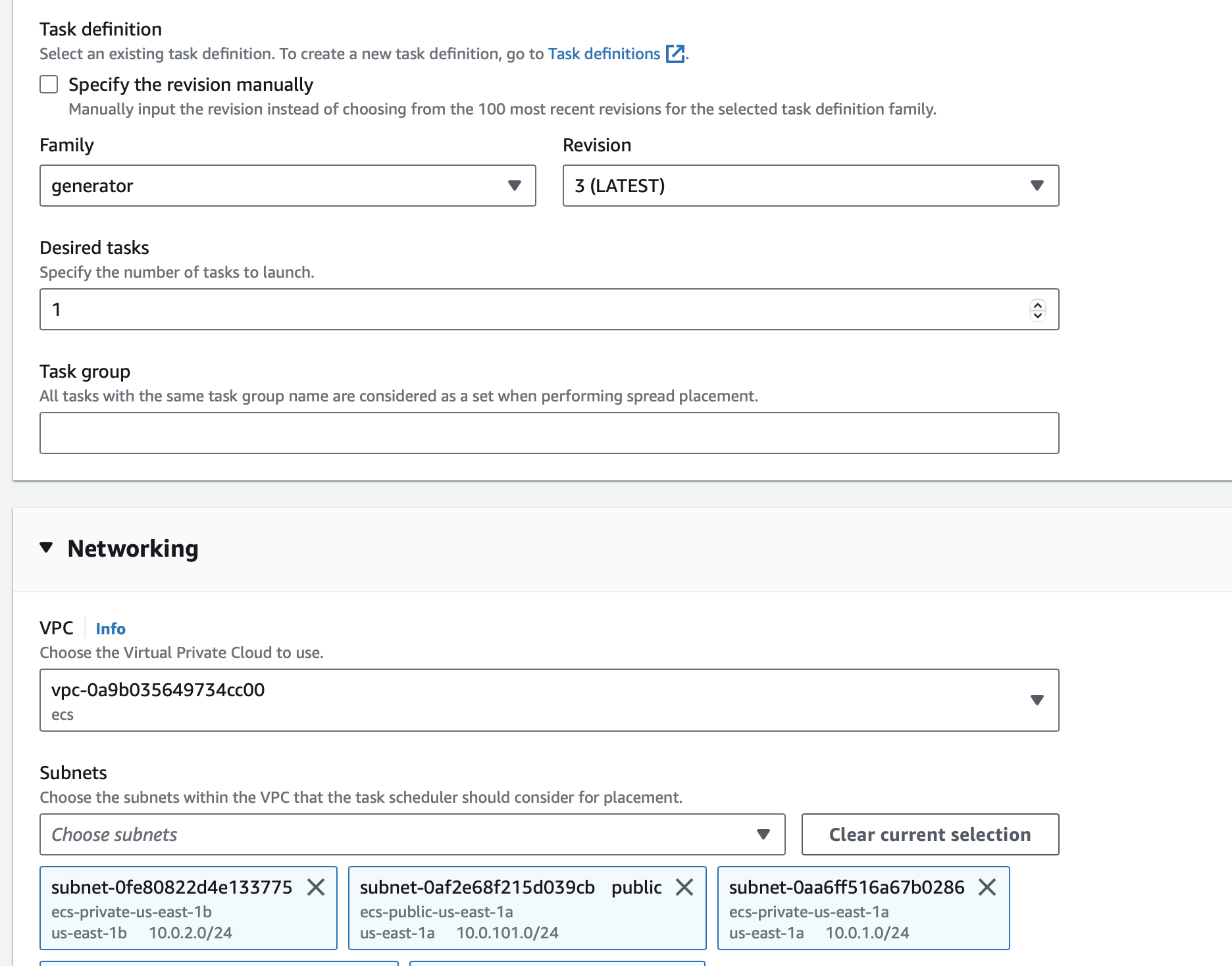
resource "aws_ecs_task_definition" "generator" {
family = "generator"
execution_role_arn = aws_iam_role.exec.arn
requires_compatibilities = ["FARGATE"]
network_mode = "awsvpc"
cpu = 256
memory = 512
container_definitions = jsonencode([
{
name = "generator"
image = "gcr.io/speedscale/generator:v2.3.586"
essential = true
logConfiguration = {
logDriver = "awslogs",
options = {
awslogs-create-group = "true",
awslogs-group = "ecs/generator"
awslogs-region = "us-east-1",
awslogs-stream-prefix = "ecs"
},
},
environment = [
{
name = "SNAPSHOT_ID"
value = "3420b3cd-35dc-4d37-8ce1-587afe0b2adb"
},
{
name = "TEST_CONFIG_ID"
value = "regression"
},
{
name = "CUSTOM_URL"
value = "http://notifications.ecs.local"
},
{
name = "LOCAL_REPLAY_MODE"
value = "true"
},
{
name = "SPEEDSCALE_API_KEY"
value = "yourkey"
},
{
name = "SPEEDSCALE_APP_URL"
value = "dev.speedscale.com"
},
{
name = "SUB_TENANT_NAME"
value = "default"
},
{
name = "SUB_TENANT_STREAM"
value = "dev-sstenant-external"
},
{
name = "TENANT_BUCKET"
value = "dev-sstenant-external"
},
{
name = "TENANT_REGION"
value = "us-east-1"
},
],
},
])
}
Launch task
You can launch this generator task from the AWS console or the CLI.
You'll need to specify the same networking and scheduling parameters as the rest of your ECS Services through the wizard shown here.
This will create a test reprt that you can view in the Speedscale dashboard.
Using Mocks
After capturing traffic and creating a snapshot, we can use a snapshot to create mocks for our service. We're going to do the following:
- Setup an init container and configure our app to trust certs just like above
- Add a
respondersidecar that will provide mocks for your app. This sidecar will have a set of environment variables to be filled from your~/.speedctl/configjust like we did when setting up theforwarderas well as two additional ones:SNAPSHOT_IDwhich comes from the snapshot created before and aTEST_CONFIG_IDwhich specifies the behavior of your mocks. - We're also adding a
redissidecar that's needed by theresponder.
resource "aws_ecs_task_definition" "with-responder" {
family = "notifications-with-responder"
execution_role_arn = aws_iam_role.exec.arn
task_role_arn = aws_iam_role.exec.arn
network_mode = "awsvpc"
requires_compatibilities = ["FARGATE"]
cpu = 256
memory = 512
container_definitions = jsonencode([
{
entrypoint = ["bash"]
command = ["-c", "aws secretsmanager get-secret-value --secret-id tls.crt --query SecretString --output text >> /etc/ssl/speedscale/tls.crt && aws secretsmanager get-secret-value --secret-id tls.key --query SecretString --output text >> /etc/ssl/speedscale/tls.key"],
mountPoints = [
{
containerPath = "/etc/ssl/speedscale",
sourceVolume = "speedscale"
}
],
logConfiguration = {
logDriver = "awslogs",
options = {
awslogs-create-group = "true",
awslogs-group = "ecs/init"
awslogs-region = "us-east-1",
awslogs-stream-prefix = "ecs"
},
},
image = "amazon/aws-cli:2.8.4",
essential = false,
name = "init"
},
{
name = "notifications"
image = "gcr.io/speedscale-demos/notifications"
essential = true
logConfiguration = {
logDriver = "awslogs",
options = {
awslogs-create-group = "true",
awslogs-group = "ecs/notifications"
awslogs-region = "us-east-1",
awslogs-stream-prefix = "ecs"
},
},
environment = [
{
name = "SSL_CERT_FILE"
value = "/etc/ssl/speedscale/tls.crt"
},
{
name = "HTTP_PROXY"
value = "http://localhost:4140"
},
{
name = "HTTPS_PROXY"
value = "http://localhost:4140"
},
],
dependsOn = [
{
containerName = "init",
condition = "SUCCESS"
}
]
portMappings = [
{
containerPort = 8080
}
]
mountPoints = [
{
containerPath = "/etc/ssl/speedscale",
sourceVolume = "speedscale"
}
],
},
{
name = "responder"
image = "gcr.io/speedscale/responder:v2.3.586"
essential = true
healthCheck = {
command = [
"CMD-SHELL",
"curl -v localhost:4140/speedscale/ready || exit 1"
]
}
logConfiguration = {
logDriver = "awslogs",
options = {
awslogs-create-group = "true",
awslogs-group = "ecs/responder"
awslogs-region = "us-east-1",
awslogs-stream-prefix = "ecs"
},
},
environment = [
{
name = "SNAPSHOT_ID"
value = "77a8279e-79b0-4140-b585-9e36b78818bb"
},
{
name = "TEST_CONFIG_ID"
value = "regression"
},
{
name = "SPEEDSCALE_API_KEY"
value = "yourkey"
},
{
name = "SPEEDSCALE_APP_URL"
value = "app.speedscale.com"
},
{
name = "SUB_TENANT_NAME"
value = "default"
},
{
name = "SUB_TENANT_STREAM"
value = "sstenant-tenant"
},
{
name = "TENANT_BUCKET"
value = "sstenant-tenant"
},
{
name = "TENANT_REGION"
value = "us-east-1"
},
{
name = "SERVICE_HTTP_PORT"
value = "4140"
},
{
name = "REDIS_SERVICE_HOST"
value = "localhost"
},
{
name = "REDIS_SERVICE_PORT"
value = "6379"
},
{
name = "REDIS_SERVICE_PASS"
value = "redis-pass"
},
{
name = "PASSTHROUGH"
value = "true"
},
]
dependsOn = [
{
containerName = "init",
condition = "SUCCESS"
},
]
portMappings = [
{
containerPort = 4140
},
{
containerPort = 8443
},
{
containerPort = 27017
},
{
containerPort = 5432
},
{
containerPort = 5672
},
]
mountPoints = [
{
containerPath = "/etc/ssl/speedscale",
sourceVolume = "speedscale"
}
],
},
{
name = "redis"
image = "gcr.io/speedscale/redis"
essential = true
logConfiguration = {
logDriver = "awslogs",
options = {
awslogs-create-group = "true",
awslogs-group = "ecs/redis"
awslogs-region = "us-east-1",
awslogs-stream-prefix = "ecs"
},
},
portMappings = [
{
containerPort = 6379
}
]
environment = [
{
name = "ALLOW_EMPTY_PASSWORD"
value = "no"
},
{
name = "REDIS_AOF_ENABLED"
value = "no"
},
{
name = "REDIS_PORT"
value = "6379"
},
{
name = "REDIS_PASSWORD"
value = "redis-pass"
}
]
},
],
)
volume {
name = "speedscale"
}
}
Modify the ECS service
Now the ECS service needs to be modified to use the new task definition and the load balancer configuration needs to point to notifications:8080 again instead of goproxy as it did during capture.
resource "aws_ecs_service" "notifications" {
name = "notifications"
cluster = aws_ecs_cluster.cluster.id
task_definition = aws_ecs_task_definition.with-speedscale.arn
force_new_deployment = true
desired_count = 1
launch_type = "FARGATE"
load_balancer {
target_group_arn = aws_lb_target_group.default.arn
container_name = "notifications"
container_port = 8080
}
network_configuration {
subnets = data.aws_subnet_ids.private.ids
security_groups = [var.sg_id]
}
}
Verification
Now if you send requests to your app as you did previously through the load balancer, your app will use mocks provided by Speedscale instead of making external API calls.