Google Cloud Run
This workflow is currently in preview status. Speedscale currently works best inside plain Kubernetes clusters such as EKS and GKE.
Prerequisites
Working with Google Cloud Run
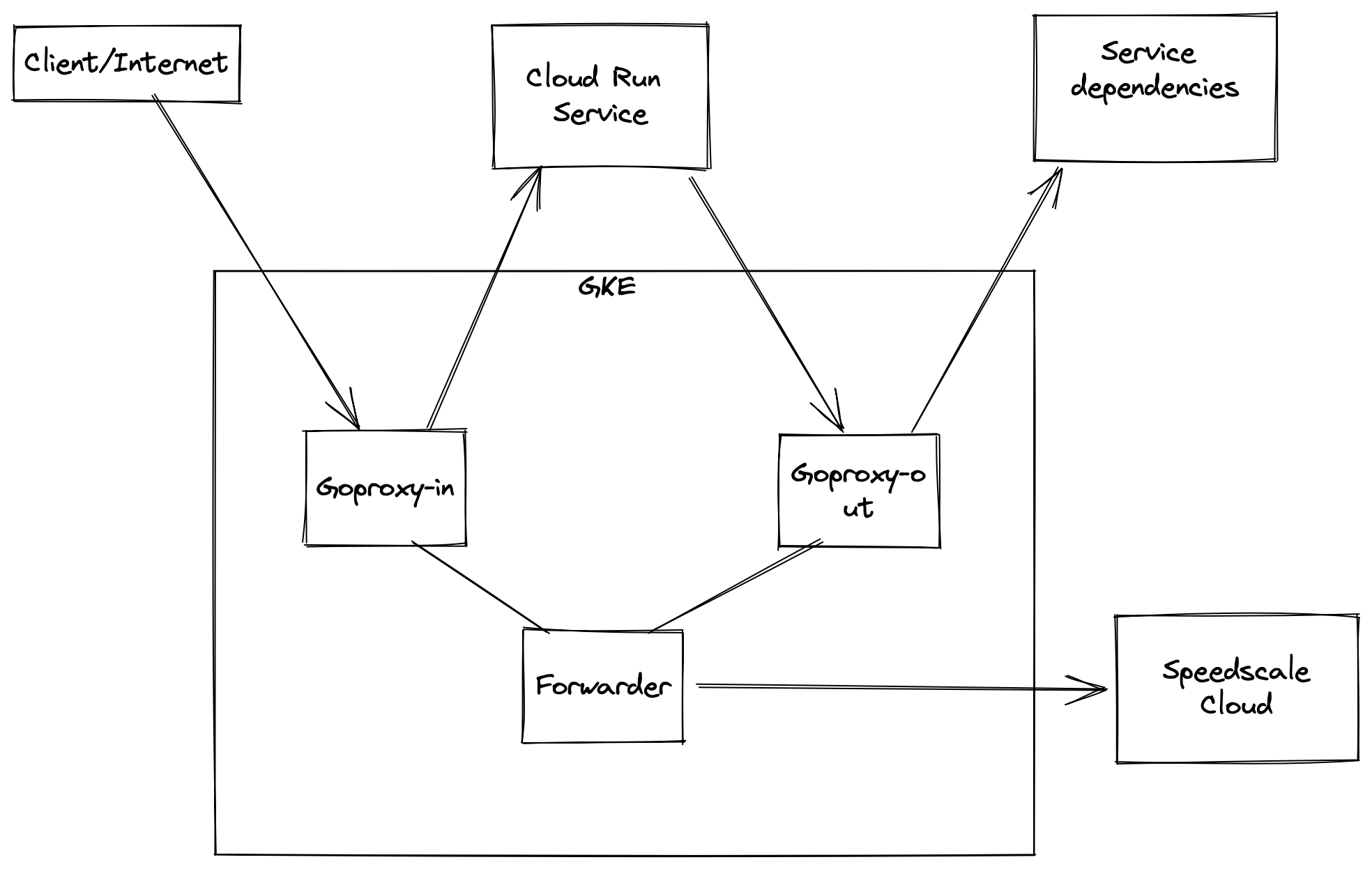
In order to capture traffic from Cloud Run, we need to set up a few components shown in the diagram above.
Create a cluster
We need to create a GKE cluster in order to run our proxy and forwarding components. Follow the prompts in the Google Cloud console to create a standard GKE cluster. Do not create an Autopilot cluster. All other standard settings should be fine. Cluster creation can take a few minutes and we need to wait till it's finished in order to deploy Speedscale components to it. Once it's done, setup kubectl access by running
gcloud container clusters get-credential <cluster-name> --region <region>
Deploy Speedscale components
Now that the cluster is set up, deploy the needed components by applying the provided manifests. We'll need to modify the manifests with custom values from ~/.speedctl/config. Replace the following values in the capture.yaml:
APP_LABEL,APP_POD_NAME,APP_POD_NAMESPACEwith your app nameREVERSE_PROXY_HOSTwith the full URL of your cloud run app
Then run
helm install speedscale-operator speedscale/speedscale-operator \
-n speedscale \
--create-namespace \
--set apiKey=<YOUR-SPEEDSCALE-API-KEY> \
--set clusterName=<YOUR-CLUSTER-NAME>
kubectl create ns capture
kubectl -n speedscale get secret speedscale-certs -o json | jq -r '.data["tls.crt"]' | base64 -D >> tls.crt
kubectl -n speedscale get secret speedscale-certs -o json | jq -r '.data["tls.key"]' | base64 -D >> tls.key
kubectl -n capture create secret tls tls-certs --cert=tls.crt --key=tls.key
kubectl apply -f capture.yaml
Now you'll need the IP of the goproxy instance you just created which you can get by running
kubectl -n capture get svc goproxy-capture
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
goproxy-capture LoadBalancer 10.2.4.180 35.222.2.222 8080:30116/TCP,8081:31841/TCP 101m
Grab the external IP (35.222.2.222 here). It may take some time to show up as a TCP Load Balancer is provisioned when you deploy the manifests.
This step also creates a Network Endpoint Group (NEG) that can be used as a backend in a Load Balancer.
kubectl -n capture describe svc goproxy
Name: goproxy
Namespace: speedscale
Labels: app=goproxy
Annotations: cloud.google.com/neg: {"exposed_ports": {"8080":{}, "8081":{}}}
cloud.google.com/neg-status:
{"network_endpoint_groups":{"8081":"k8s1-0fb6446b-speedscale-goproxy-8081-e0c33991","8080":"k8s1-0fb6446b-speedscale-goproxy-8080-7e876f3b...
networking.gke.io/load-balancer-type: Internal
If you are using a Load Balancer to route to your Cloud Run service, you will need to configure it to use the backend NEG for 8080 in this case called k8s1-0fb6446b-speedscale-goproxy-8080-7e876f3b....
Create the Google secret
In order to establish TLS connections to our proxy, we'll need to add the TLS cert to our trust store. We'll use Google Secret Manager to do this.
gcloud secrets create speedscale-certs --replication-policy="automatic"
gcloud secrets versions add speedscale-certs --data-file=tls.crt
This pulls the TLS cert from Kubernetes and creates the same secret in Google Secret Manager. It is now available for our Cloud Run app to use.
Configure the Cloud Run app
Now that all our infrastructure is setup, we can modify our app to capture traffic. In Cloud Run, navigate to the app and in the YAML tab, hit edit. We're going to add the env variables and mount the secret we created in the above step. The ports and resources section are shown just to indicate the level of indentation needed for our settings. Make sure to replace the IP in proxy settings to the one we grabbed from the Kubernetes service above (the port will remain unchanged ie. 8081).
containers:
- image: gcr.io/speedscale-demos/payment
ports:
- name: http1
containerPort: 8080
env:
- name: SSL_CERT_FILE
value: /etc/ssl/speedscale/tls.crt
- name: HTTP_PROXY
value: http://35.222.2.222:8081
- name: HTTPS_PROXY
value: http://35.222.2.222:8081
resources:
limits:
cpu: 1000m
memory: 512Mi
volumeMounts:
- name: tls
readOnly: true
mountPath: /etc/ssl/speedscale
volumes:
- name: tls
secret:
secretName: speedscale-certs
items:
- key: latest
path: tls.crt
The environment variables depend on the language of your app so refer to proxy server configuration and trusting TLS certificates.
Verification
Now if you run curl http://35.222.2.222:8080/<some path for your app>, you should be able to access your Cloud Run app and also see the traffic in Speedscale.
Running Replays
Replays can be run against the service through the Kubernetes cluster as detailed here. The HTTP Proxy settings and TLS settings set on the Cloud Run service above need to remain as is. It's recommended to set the collect-logs option to false since the Kubernetes service logs are not relevant in this setup.
Note that the CPU and memory graphs displayed in the report will be those for the proxy container and not the actual cloud run service.
Do not set the cleanup mode setting (replay.speedscale.com/cleanup) to all as this will delete the proxy container which is acting as the entrypoint and HTTP Proxy for your Cloud Run app.
Advanced setup
This setup assumes the Cloud Run service being instrumented is available publicly. If you want to make the service load balancer internal only, you can add this annotation networking.gke.io/load-balancer-type: "Internal" to the Kubernetes service definition. This requires the Cloud Run service to be on the same VPC as the GKE cluster and requires you to connect your Cloud Run app to your VPC as detailed here
Manifest
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: goproxy-capture
name: goproxy-capture
namespace: capture
spec:
progressDeadlineSeconds: 600
replicas: 1
revisionHistoryLimit: 10
selector:
matchLabels:
app: goproxy-capture
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: goproxy-capture
spec:
containers:
- image: gcr.io/speedscale/goproxy:v2.3.586
imagePullPolicy: Always
name: goproxy-capture
env:
- name: APP_LABEL
value: payment
- name: APP_POD_NAME
value: payment
- name: APP_POD_NAMESPACE
value: payment
- name: CAPTURE_MODE
value: proxy
- name: FORWARDER_ADDR
value: speedscale-forwarder.speedscale.svc:80
- name: PROXY_TYPE
value: dual
- name: PROXY_PROTOCOL
value: http
- name: TLS_OUT_UNWRAP
value: "true"
- name: TLS_CERT_DIR
value: /etc/ssl/capture
- name: REVERSE_PROXY_HOST
value: "https://payment-cloud-run.a.run.app"
- name: REVERSE_PROXY_PORT
value: "443"
- name: PROXY_IN_PORT
value: "8080"
- name: PROXY_OUT_PORT
value: "8081"
- name: LOG_LEVEL
value: info
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
name: proxy-in
protocol: TCP
- containerPort: 8081
name: proxy-out
protocol: TCP
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /etc/ssl/capture
name: tls-out
readOnly: true
resources: {}
securityContext:
readOnlyRootFilesystem: false
runAsGroup: 2102
runAsUser: 2102
terminationMessagePath: /dev/termination-log
terminationMessagePolicy: File
volumes:
- name: tls-out
secret:
defaultMode: 420
optional: false
secretName: tls-certs
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app: goproxy-capture
name: goproxy-capture
namespace: capture
annotations:
cloud.google.com/neg: '{"exposed_ports": {"8080":{}, "8081":{}}}'
spec:
ports:
- name: in
port: 8080
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 8080
- name: out
port: 8081
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 8081
selector:
app: goproxy-capture
type: LoadBalancer