CI/CD
Integrate proxymock into your CI/CD workflow to enable high-velocity deployment with confidence.
Run proxymock after your build and unit tests, but before deploying to production.
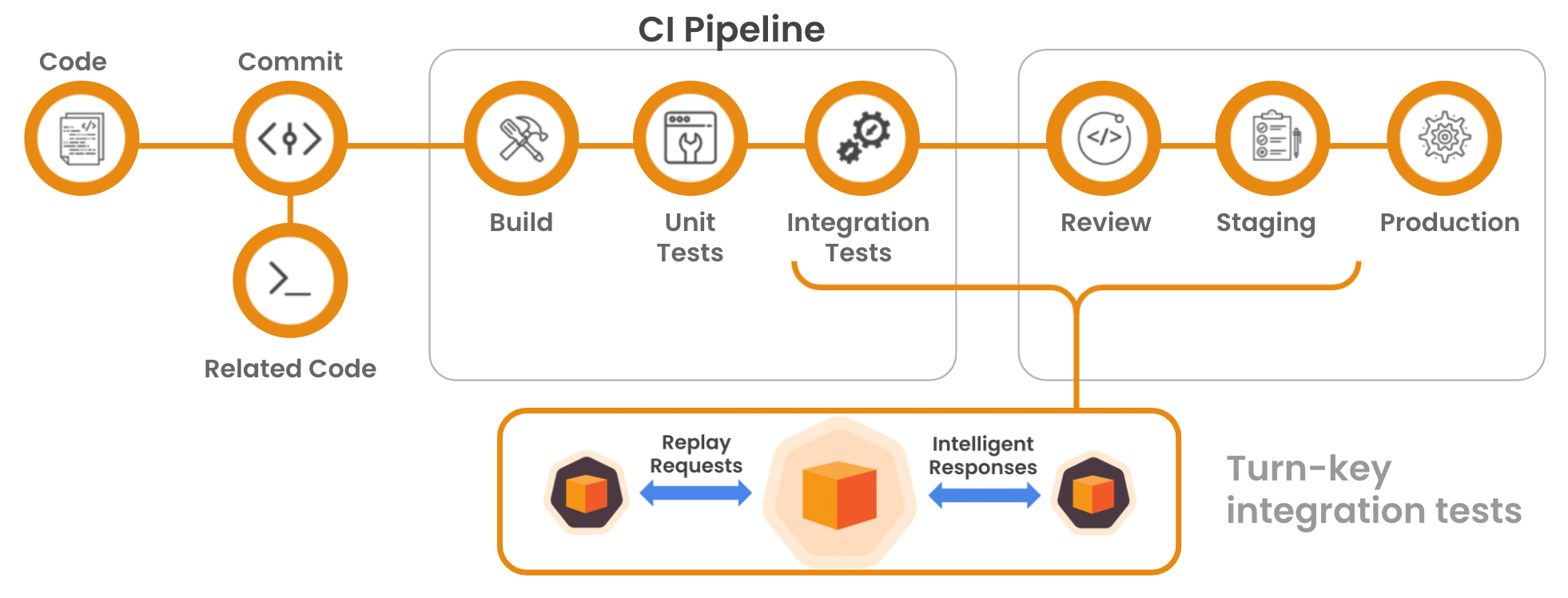
Adding anything to your CI/CD pipeline generally involves the same 3 steps:
- Adding a step to your pipeline (see #1. The Pipeline)
- Executing the right script to perform a desired action (see #2. The Script)
- Authentication (see #3. The API Key)
Prerequisites
In order to integrate proxymock into your CI/CD you will need:
- Access to modify your CI/CD pipeline
- Your proxymock API key
- A paid proxymock account (see proxymock.io for pricing details)
- Pre-recorded traffic files (see recording to record from your app)
1. The Pipeline
These pipeline examples contain the minimal configuration needed to run proxymock with your application.
Examples build a Go binary using go build using the golang container image.
Your image can be anything you choose as long as proxymock has access to
your application.
- GitHub
- GitLab
- Jenkins
- Azure DevOps
- Google Cloud Deploy with Skaffold
- AWS CodeBuild
- Bitbucket Pipelines
- TeamCity
- CircleCI
name: CI with proxymock
on:
push:
branches:
- main
pull_request:
branches:
- main
jobs:
test:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
container: golang:1.25
steps:
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Build and test with proxymock
run: |
go build -o myapp .
./proxymock.sh # <--- proxymock script - see below
stages:
- build
# build Go application and test with proxymock
build:
stage: build
image: golang:1.25
script:
- go build -o myapp .
- ./proxymock.sh # <--- proxymock script - see below
#!groovy
pipeline {
agent {
docker { image 'golang:1.25' }
}
stages {
stage('Build and Test') {
steps {
sh 'go build -o myapp .'
sh './proxymock.sh' // <--- proxymock script - see below
}
}
}
post{
success{
echo "======== pipeline executed successfully ========"
}
failure{
echo "======== pipeline execution failed ========"
}
}
}
trigger:
- main
pool:
vmImage: "ubuntu-latest"
container: golang:1.25
steps:
- script: |
go build -o myapp .
./proxymock.sh # <--- proxymock script - see below
displayName: 'Build and test with proxymock'
Add the verify block to your existing Skaffold deploy.
apiVersion: skaffold/v4beta13
kind: Config
manifests:
rawYaml:
- k8s-deploy.yaml
deploy:
kubectl: {}
build:
artifacts:
- image: myapp
docker:
dockerfile: Dockerfile
verify:
- name: speedscale
container:
name: speedscale
image: golang:1.25
command: ["/bin/bash"]
args: ["-c", "go build -o myapp . && ./proxymock.sh"] # <--- proxymock script - see below
See https://skaffold.dev/docs/references/yaml/ for spec details.
version: 0.2
phases:
install:
runtime-versions:
golang: 1.25
build:
commands:
- go build -o myapp .
- ./proxymock.sh # <--- proxymock script - see below
artifacts:
files:
- myapp
image: golang:1.25
pipelines:
default:
- step:
name: Build and test with proxymock
script:
- go build -o myapp .
- ./proxymock.sh # <--- proxymock script - see below
import jetbrains.buildServer.configs.kotlin.*
import jetbrains.buildServer.configs.kotlin.buildSteps.script
object Build : BuildType({
name = "Build and Test"
requirements {
contains("docker.server.version")
}
steps {
script {
name = "Build and test with proxymock"
dockerImage = "golang:1.25"
scriptContent = """
go build -o myapp .
./proxymock.sh # <--- proxymock script - see below
""".trimIndent()
}
}
})
version: 2.1
jobs:
speedscale:
docker:
- image: "golang:1.25"
steps:
- checkout
- run:
name: Build Go application
command: go build -o myapp .
- run:
name: Run proxymock tests
command: ./proxymock.sh # <--- proxymock script - see below
See a full config.yml for more context.
2. The Script
Let's fill in the proxymock.sh script shown above. Be sure to customize the user settings at the top of the script.
The script expects the SPEEDSCALE_API_KEY environment variable to be set
(securely) for authentication. See The API Key.
#!/usr/bin/env bash
# set the port your application will listen on, where traffic will be replayed
APP_PORT=8080
# set the command to run your application. ensure this command has all of the
# correct flags and that the environment has all of the configuration needed to
# run your application properly
APP_COMMAND="./my-example-app --log-level debug" # CHANGE ME!
# the path to pre-recorded proxymock traffic
PROXYMOCK_IN_DIR="proxymock"
# optionally, run mock server
RUN_MOCK_SERVER=true
###########################
### USER SETTINGS ABOVE ###
### SCRIPT BELOW ###
###########################
# log file paths
REPLAY_LOG_FILE="proxymock_replay.log"
APP_LOG_FILE="proxymock_app.log"
MOCK_LOG_FILE="proxymock_mock.log"
set -e
set -o pipefail 2>/dev/null || true
validate() {
if [ -z "$SPEEDSCALE_API_KEY" ]; then
echo "ERROR: SPEEDSCALE_API_KEY environment variable is not set"
exit 1
fi
if [ ! -d "$PROXYMOCK_IN_DIR" ]; then
echo "ERROR: $PROXYMOCK_IN_DIR does not exist - make sure you have pre-recorded traffic to mock / replay"
exit 1
fi
}
install_proxymock() {
echo "Installing proxymock..."
sh -c "$(curl -Lfs https://downloads.speedscale.com/proxymock/install-proxymock)"
export PATH=${PATH}:${HOME}/.speedscale
# initialize with API key
proxymock init --api-key "$SPEEDSCALE_API_KEY"
}
run_mock_server() {
echo "Starting mock server..."
proxymock mock \
--verbose \
--in "$PROXYMOCK_IN_DIR/" \
--log-to "$MOCK_LOG_FILE" &
}
run_replay() {
print_logs() {
if [ -f "$MOCK_LOG_FILE" ]; then
echo "=== proxymock mock server logs ==="
cat $MOCK_LOG_FILE
fi
echo "=== proxymock replay logs ==="
cat $REPLAY_LOG_FILE
if [ -f "$APP_LOG_FILE" ]; then
echo "=== application logs ==="
cat $APP_LOG_FILE
fi
}
trap print_logs EXIT
# start proxymock replay, with your app, to run your app and replay test traffic
# against it
proxymock replay \
--in "$PROXYMOCK_IN_DIR" \
--test-against localhost:$APP_PORT \
--log-to $REPLAY_LOG_FILE \
--app-log-to $APP_LOG_FILE \
--fail-if "latency.max > 1500" \
-- $APP_COMMAND
}
main() {
validate
install_proxymock
if [ "$RUN_MOCK_SERVER" = "true" ]; then
run_mock_server
fi
run_replay
}
main
3. The API Key
proxymock requires a valid API key to run. Your API key is created when you
first run proxymock init and is stored in a config file, at
$HOME/.speedscale/config.yaml by default.
To make it easy, once registered you can get your API key directly with some command line magic:
SPEEDSCALE_CONFIG_FILE=$(proxymock version | grep 'Config File' | awk '{print $3}')
SPEEDSCALE_API_KEY=$(cat $SPEEDSCALE_CONFIG_FILE | grep apikey | awk '{print $2}')
echo $SPEEDSCALE_API_KEY
If this does not produce an API key make sure you are registered first with proxymock init.
Make SPEEDSCALE_API_KEY available to your pipeline as an environment variable
so proxymock can be initialized when the pipeline runs.
Need Help?
Let us know on the community Slack if instructions for your deploy system are not included here.