Quickstart (CLI)
This guide provides a step-by-step approach to creating a mock server and tests for a simple Go application using only the proxymock CLI.
Choose Your Environment
Select your environment below and all instructions will update accordingly. If you prefer to run everything locally pick your operating system. If you want to access a pre-built environment in the cloud check out GitHub Codespaces.
- 🍎 macOS
- 🐧 Linux
- ☁️ Codespaces
- 🔧 Other
You've selected macOS. All commands below are optimized for macOS systems.
You've selected Linux. All commands below are optimized for Linux systems.
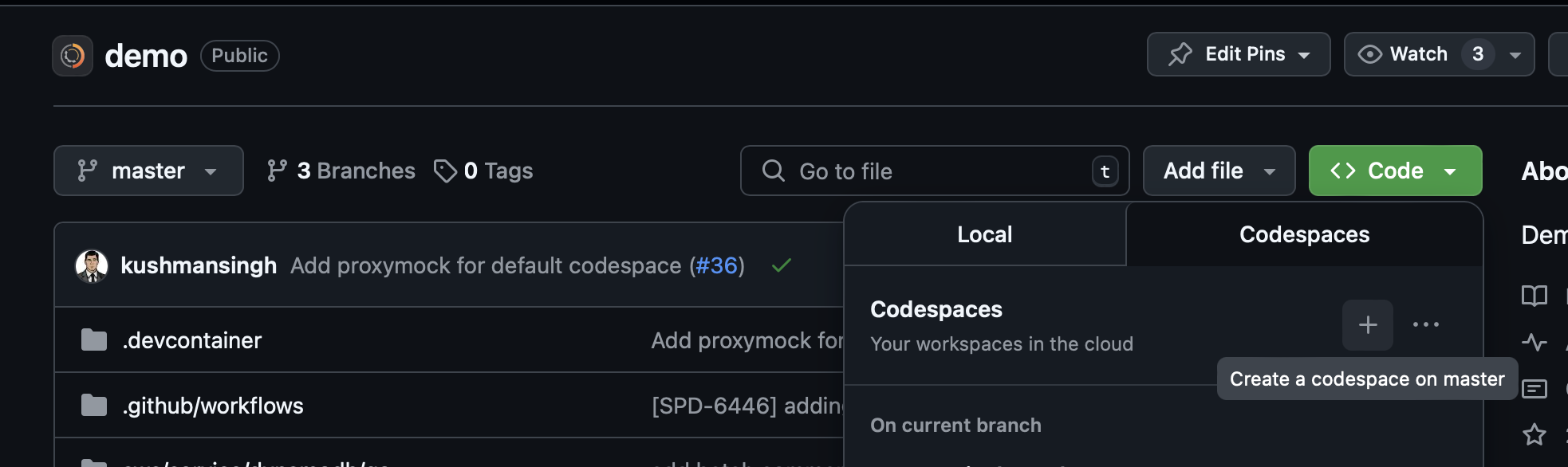
You've selected GitHub Codespaces. All commands below are optimized for the Codespaces environment with special notes for port forwarding and authentication.
Setting up Codespaces
To get started with the outerspace-go Codespace:
- Go to github.com/speedscale/outerspace-go
- Click the green "Code" button
- Select the "Codespaces" tab
- Click "Create codespace on main"
- Wait for the environment to initialize (usually 1-2 minutes)
- Once ready, you'll have a VS Code environment in your browser with Go and ProxyMock pre-installed
You've selected Other. See our detailed installation guide for your specific system.
Before you begin
- 🍎 macOS
- 🐧 Linux
- ☁️ Codespaces
- 🔧 Other
Make sure you have:
- A terminal or command prompt open to run proxymock
- A separate terminal or command prompt open to run the demo app
- go version 1.23.1 or newer installed
Make sure you have:
- A terminal or command prompt open to run proxymock
- A separate terminal or command prompt open to run the demo app
- go version 1.23.1 or newer installed
Make sure you have:
- A GitHub account with access to Codespaces
- The outerspace-go Codespace running (note that go and proxymock are pre-installed)
- Two terminal windows open in your Codespace
Make sure you have:
- A terminal or command prompt open to run proxymock
- A separate terminal or command prompt open to run the demo app
- go version 1.23.1 or newer installed
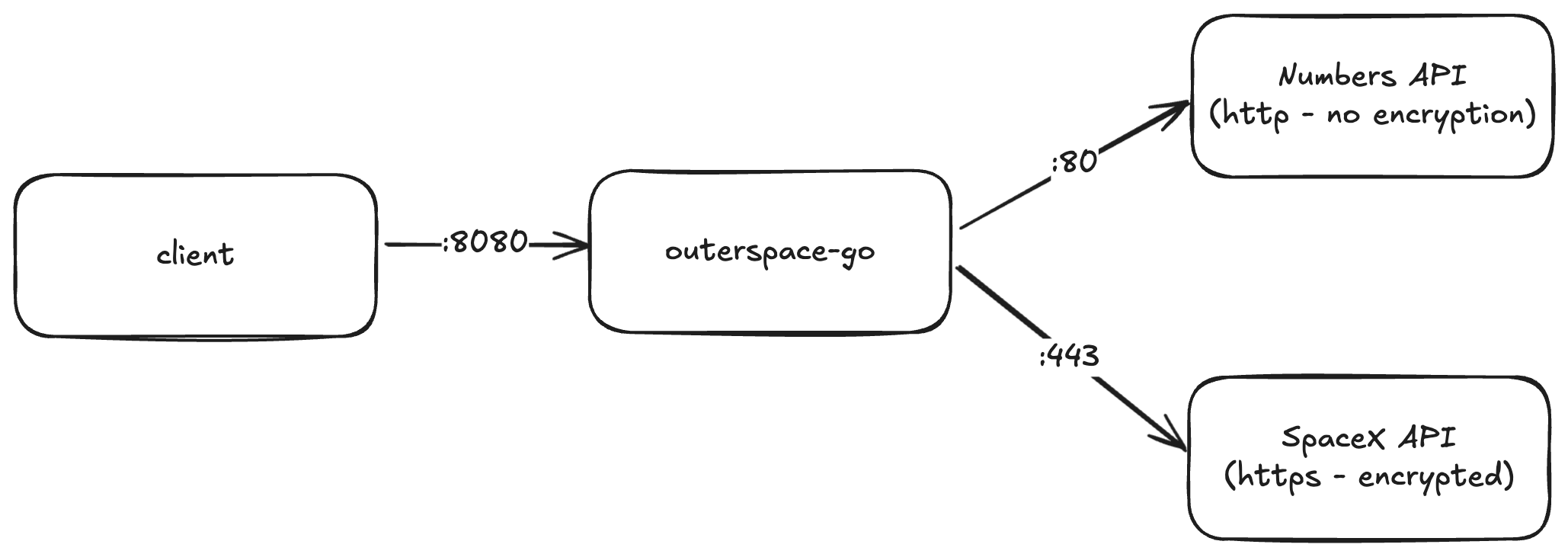
For this example we'll be using a simple demo app that accepts an API request, calls two downstream APIs and returns the results.
Step 1: Install proxymock
- 🍎 macOS
- 🐧 Linux
- ☁️ Codespaces
- 🔧 Other (Detailed)
Install with Homebrew:
brew install speedscale/tap/proxymock
Run the install script:
sh -c "$(curl -Lfs https://downloads.speedscale.com/proxymock/install-proxymock)"
No need to run any install scripts:
ProxyMock is automatically available in the outerspace-go Codespace.
For other operating systems and more detailed instructions, see the installation instructions.
Need another OS like Windows or are you having issues? See advanced installation.
Step 2: Obtain an API Key
If you are an enterprise customer you can find your api key on the Profile Page.
Otherwise you can sign up for an API Key. Don't worry, we don't sell marketing data or give your email address to any bot nets.
Step 3: Initialize proxymock
Run the following command to obtain an API key:
proxymock init --api-key <your key>
Step 4: Install the demo app and start recording
- 🍎 macOS
- 🐧 Linux
- ☁️ Codespaces
- 🔧 Other (Detailed)
git clone https://github.com/speedscale/outerspace-go && cd outerspace-go && proxymock record -- go run main.go
git clone https://github.com/speedscale/outerspace-go && cd outerspace-go && proxymock record -- go run main.go
If you're using the outerspace-go Codespace, the repository is already cloned. Navigate to it and start recording:
export SSL_CERT_FILE="${HOME}/.speedscale/certs/tls.crt"
proxymock record -- go run main.go
git clone https://github.com/speedscale/outerspace-go && cd outerspace-go && proxymock record -- go run main.go
By running this you will start proxymock in recording mode while it runs the app as a child process. Now proxymock is now listening on port 4343 for incoming traffic. This traffic will be forwarded to the demo app running at 8080. You'll see first the proxymock logs then a line across the screen, then the logs for outerspace-go. It should look something like this:
$ proxymock record -- go run main.go
proxymock output will be redirected to proxymock/recorded-2025-07-30_15-19-11.417616Z/proxymock.log
Press ctrl-c to interrupt
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
2025/07/30 15:19:12 Starting HTTP server on :8080
2025/07/30 15:19:13 Starting gRPC server on :50053
Step 4: Run test transactions
Start a new terminal and run the following command.
- 🍎 macOS
- 🐧 Linux
- ☁️ Codespaces
- 🔧 Other (Detailed)
cd outerspace-go && ./tests/run_http_tests.sh --recording
cd outerspace-go && ./tests/run_http_tests.sh --recording
./tests/run_http_tests.sh --recording
Make sure port 4343 is forwarded in your Codespace. You should see it automatically forwarded in the Ports tab.
cd outerspace-go && ./tests/run_http_tests.sh --recording
You will now see a set of output from the tests:
$ ./tests/run_http_tests.sh --recording
Recording mode enabled, using port 4143
Testing http://localhost:4143/... OK (200)
Testing http://localhost:4143/api/numbers... OK (200)
Testing http://localhost:4143/api/latest-launch... OK (200)
Testing http://localhost:4143/api/rockets... OK (200)
Testing http://localhost:4143/api/rocket?id=5e9d0d96eda699382d09d1ee... OK (200)
Http tests passed.
You can now press CTRL-C in the proxymock record terminal window to shut down recording.
You will also see some additional output in the original proxymock terminal window showing requests were handled by the demo app:
2025-07-30T15:31:57-04:00 INF Inbound latency=0.080292 method=GET path=/ query=
2025-07-30T15:31:57-04:00 INF X-Header found header=X-Numbers-Api-Type values=["math"]
2025-07-30T15:31:57-04:00 INF X-Header found header=X-Powered-By values=["Express"]
2025-07-30T15:31:57-04:00 INF X-Header found header=X-Numbers-Api-Number values=["1804"]
2025-07-30T15:31:57-04:00 INF Outbound host=numbersapi.com latency=64.452875 method=GET status=200
...
Step 5: View recording results
There should be a new directory in the proxymock subdirectory inside outerspace-go.
ls proxymock
# Output shows recorded directories like:
# recorded-2025-07-30_15-31-43.701537Z
The traffic you just recorded is contained in the most recent directory. In this case that's recorded-2025-07-30_15-31-43.701537Z but it will change based on the date of recording. Each API request can be inspected as a markdown file:
$ cat proxymock/recorded-2025-07-30_15-31-43.701537Z/localhost/2025-07-30_19-56-08.410226Z.md
### REQUEST (TEST) ###
``
GET http://localhost:4143/ HTTP/1.1
Accept: */*
Host: localhost:4143
User-Agent: curl/8.7.1
...
Step 6: Run mock server and tests
Go back to your original terminal (running proxymock record), stop proxymock by running CTRL-C and then start a mock server:
- 🍎 macOS
- 🐧 Linux
- ☁️ Codespaces
- 🔧 Other (Detailed)
proxymock mock -- go run main.go
proxymock mock -- go run main.go
proxymock mock -- go run main.go
proxymock mock -- go run main.go
Your demo app will now start using the local mock server.
When running proxymock mock your app no longer requires access to backend systems. The app will talk locally to proxymock instead of outside APIs.
Now exercise your demo app by running the same tests we ran before - except using the recording instead of a script. proxymock takes the recorded inbound requests and re-uses them as tests.
Open your second terminal window and run the following:
- 🍎 macOS
- 🐧 Linux
- ☁️ Codespaces
- 🔧 Other (Detailed)
proxymock replay --test-against http://localhost:8080
proxymock replay --test-against http://localhost:8080
proxymock replay --test-against http://localhost:8080
proxymock replay --test-against http://localhost:8080
The proxymock replay command will now run the original inbound transactions directly against your demo app. The demo app no longer requires downstream systems for these tests as they are being simulated by proxymock. You should see a summary table like this:
LATENCY / THROUGHPUT
+--------------------+--------+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+------------+
| ENDPOINT | METHOD | AVG | P50 | P90 | P95 | P99 | COUNT | PCT | PER-SECOND |
+--------------------+--------+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+------------+
| / | GET | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 2 | 20.0% | 9.93 |
| /api/rockets | GET | 12.00 | 9.00 | 9.00 | 9.00 | 9.00 | 2 | 20.0% | 9.93 |
| /api/rocket | GET | 12.50 | 10.00 | 10.00 | 10.00 | 10.00 | 2 | 20.0% | 9.93 |
| /api/numbers | GET | 14.00 | 13.00 | 13.00 | 13.00 | 13.00 | 2 | 20.0% | 9.93 |
| /api/latest-launch | GET | 53.50 | 14.00 | 14.00 | 14.00 | 14.00 | 2 | 20.0% | 9.93 |
+--------------------+--------+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+------------+
This demonstrates how you can test your microservice in isolation.
- No need to write tests, you can replay the inbound traffic
- No need to build a test environment, you can mock the dependencies
- If you want to change the data, simply edit the markdown files