PostgreSQL Mocking
This guide covers how to use proxymock to mock PostgreSQL database connections and queries for local development and testing.
Introduction to PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL is one of the world's most advanced open-source relational database management systems (RDBMS). It uses Structured Query Language (SQL) for accessing and managing data stored in relational tables. proxymock is able to record and mock PostgreSQL databases. This allows you to mock a PostgreSQL database, including real data, without running a PostgreSQL database or populating it with data. To do this, we record your app talking to a PostgreSQL database and simulate the database in subsequent tests. To learn more about proxymock recording and architecture, check out the quick start.
Demo App
The following instructions will work with most PostgreSQL clients. However, for demonstration purposes we'll use a simple gp application that connects to a PostgreSQL database. If you are using your own app skip ahead to recording for the environment variables you'll need.
This demo app is available in the speedscale/demo repository and requires Go to be installed. If you'd like to use the demo app, clone the repository and navigate to the go-postgres directory, which contains a basic golang user service that interacts with PostgreSQL:
git clone https://github.com/speedscale/demo && cd demo/go-postgres
Start PostgreSQL on your local machine (instructions in the README). Don't worry if you don't have go installed and can't use this app. Just apply the environment variables to your own PostgreSQL client app.
Recording PostgreSQL Traffic
The proxymock record command creates RRPair files from real PostgreSQL interactions. Each request will contain a PostgreSQL command (like a SELECT SQL statement) and the response will usually contain row information and values returned by the database.
Start the Recorder
Start a dedicated terminal window to run the proxymock recorder:
proxymock record --reverse-proxy 15432=localhost:5432 --app-port 8080
This tells the recorder to listen on port 15432 for PostgreSQL traffic and forward it to the real PostgreSQL server at 5432. Your can learn more about the how proxymock records on the architecture page.
PostgreSQL Connection Configuration
If you are using the demo app, make sure you have PostgreSQL running and you have created the database. The instructions are in the demo readme.
For proxymock to capture PostgreSQL traffic, configure your application to route database connections through the proxy using environment variables. Start a new terminal window that will run the demo app server:
PGUSER=<user> PGPORT=15432 go run main.go
Normally PGPORT and PGUSER will default to the default postgres installation values. With homebrew on mac that means your $username and 5432. Since proxymock is intercepting traffic on port localhost:15432 we set PGPORT to use those connection parameters. This is the key ingredient for redirecting traffic to the proxymock recorder.
What Gets Recorded
You can inspect the recording using the inspect command:
proxymock inspect
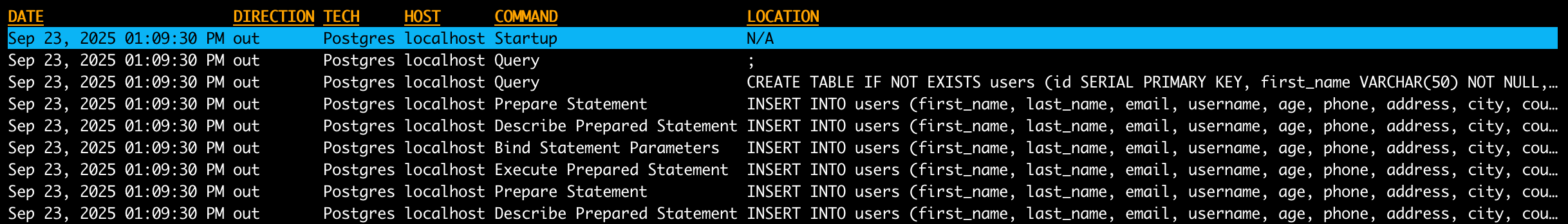
proxymock captures PostgreSQL traffic as RRPair files containing:
- Request Data: SQL queries, prepared statements, connection handshakes
- Response Data: Result sets, error responses, metadata
- Timing Information: Query execution times and connection latency
The actual wire protocol is binary but proxymock displays request and response data as JSON. The underlying files can be modified if you want your mock to return different values. You can learn more about the structure of the underlying recording by looking at the proxymock directory containing the recording files and the docs.
Troubleshooting Recording
- Ensure your PostgreSQL driver supports SOCKS5 proxy or use reverse proxy mapping
- Check that
tcp_proxyenvironment variable is set correctly - Verify PostgreSQL server is accessible from proxymock
Starting the Mock Server
Make sure to stop your local PostgreSQL server to prevent port conflicts. You can run your app against the normal PostgreSQL port 5432 now and proxymock will simulate the database.
Start the proxymock mock server:
proxymock mock
You can now run your PostgreSQL client normally and it will connect to proxymock on port 5432 like a normal database.
Modifying Responses
To modify the responses manually, you can find the appropriate markdown file and edit the contents. However, to automate data transforamtion you can use the transform system provided by Speedscale enterprise. To edit your snapshot, upload it to the cloud:
proxymock cloud push snapshot
A link to your snapshot will be provided. In the Speedscale UI, add your transforms like the following:

Remember to click Save. Now download the modified snapshot:
proxymock cloud pull snapshot <id>
You will notice a new .metadata directory containing your transform definitions. When you run proxymock mock again the transforms will be applied to your mock.